This setup guide is about building web cluster with a pair of Linux loadbalancers as frontend. It uses Linux Virtual Server(LVS) and Piranha. Piranha is a web-based gui installed in LVS Routers primarily to generating a valid /etc/lvs.cf file.
Start by installing LVS on LVS Router.
[root@lvsrouter ~]# yum groupinstall "Load Balancer"
================================================================================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
ipvsadm x86_64 1.25-10.el6 base 41 k
piranha x86_64 0.8.6-2.el6_4.1 updates 623 k
Installing for dependencies:
libedit x86_64 2.11-4.20080712cvs.1.el6 base 74 k
libnl x86_64 1.1-14.el6 base 121 k
php x86_64 5.3.3-22.el6 base 1.1 M
php-cli x86_64 5.3.3-22.el6 base 2.2 M
php-common x86_64 5.3.3-22.el6 base 524 k
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 7 Package(s)
Total download size: 4.7 M
Installed size: 18 M
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Start piranha and pulse services on reboot.
chkconfig piranha-gui on
chkconfig pulse on
Set a password for piranha web
/usr/sbin/piranha-passwd
Allow ports in iptables
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 3636 -j ACCEPT
Edit piranha config
vi /etc/sysconfig/ha/conf/httpd.conf
Start the piranha gui service
service piranha-gui start
For LVS router to forward network packets properly to real servers, each LVS router node must have IP forwarding turned on. Turn on packet forwarding by editing sysctl.conf:
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
Reload sysctl
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
Start http services on the Real Servers
service httpd start
On the LVS Router, log in to the Piranha web ui to begin configuration.
(eg http://(loadbalancer-ip):3636). Using "piranha" as user name, and key in the newly setup password.
Enter Primary Router's IP address in "Global Settings"->"Primary server public IP:".
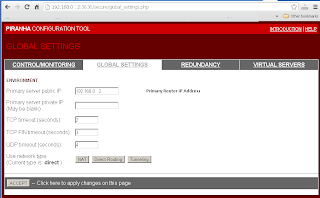
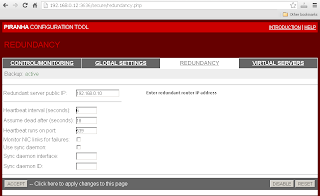
Enter Redundant Router's IP address in "Redundancy"->"Redundant server public IP:".
Enter Virtual Server settings in "Virtual Servers"->"Virtual Server".
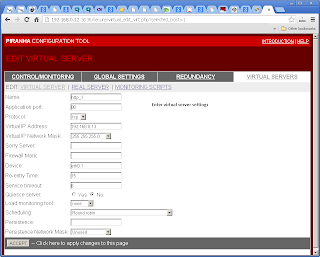
Include Real Server settings in "Virtual Servers"->"Real Server".
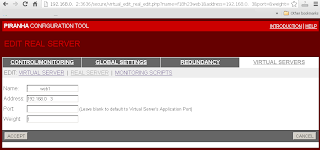
On each time the Piranha Gui was changed, have to sync the settings to Backup Routers, and restart the pulse service on both routers.
service pulse restart
To see the virtual server's statistics, use "watch ipvsadm".
[root@lvsrouter ~]# watch ipvsadm
Create arptables entry for each Virtual IP address on each Real Server(eg Webserver). You can add below command to /etc/rc.local to start on every reboot. If the network adaptor on Real Server is eth0, refer to below, if not change as according:
ip addr add (virtual ip) dev eth0:1
Direct Routing with arptables_jf. To configure each real server to ignore ARP requests for each of the virtual IP addresses the Piranha cluster services:
yum install arptables_jf
arptables -A IN -d (virtual_ip) -j DROP
arptables -A OUT -d (virtual_ip) -j mangle --mangle-ip-s (real_ip)
chkconfig arptables_jf on
service arptables_jf save
service arptables_jf restart
Create a loopback on each Real Server for monitoring Virtual IP.
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-lo:0
DEVICE=lo:0
IPADDR=(Virtual IP)
NETMASK=255.255.255.255
NETWORK=192.168.0.0
ONBOOT=yes
NAME=loopback